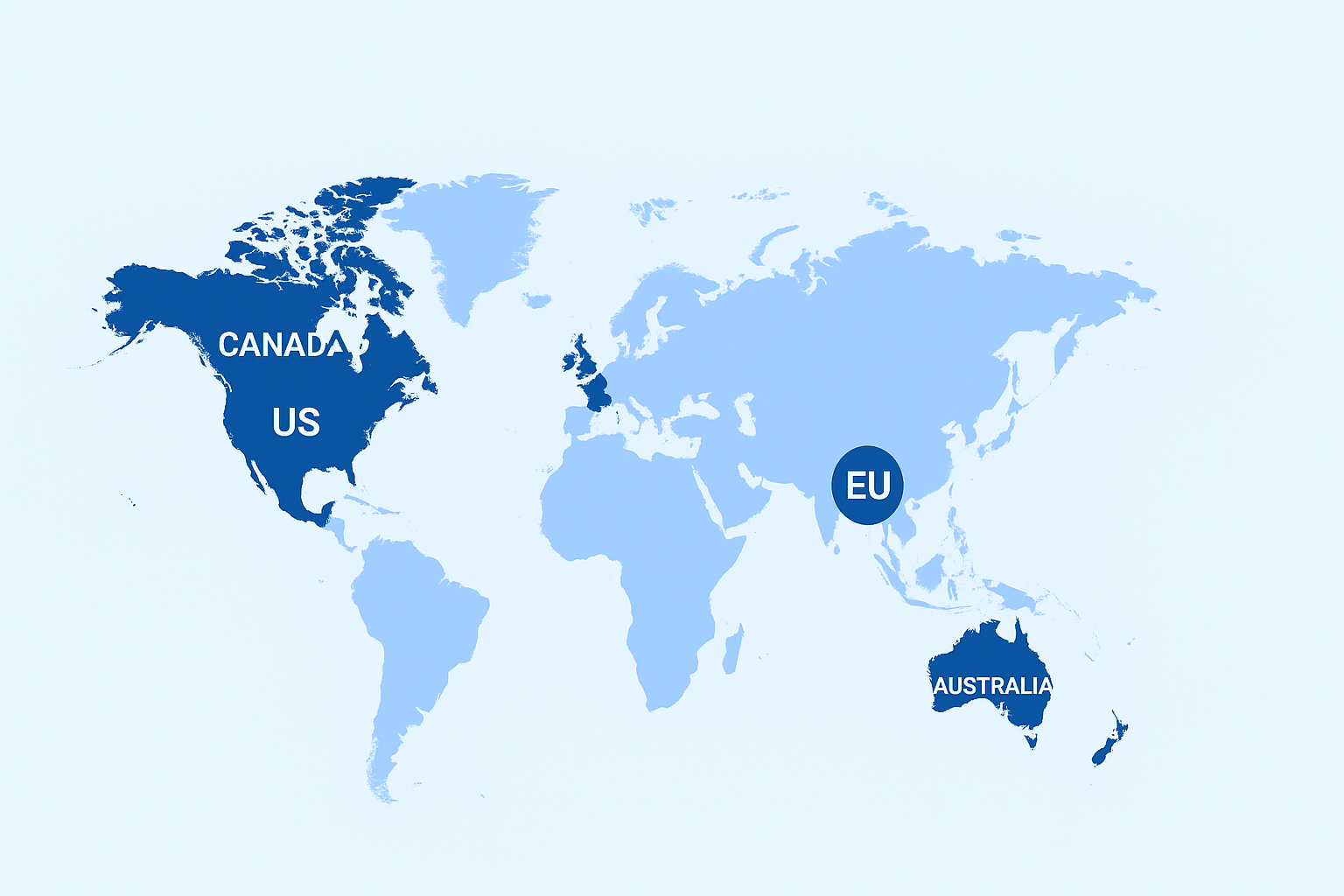
Indian students have long seen American universities as launching pads to stellar global careers. Yet in 2025, growing uncertainty around job placements, costly tuition, tightening US immigration laws during Donald Trump’s second presidency (since January 20, 2025), and lengthy green card waits are fueling debate: Is the US still the best bet for Indian aspirants seeking international education and long-term opportunities? This article offers a crisp, fact-driven comparison of the US, EU, Canada, UK, and Australia— world’s top study destinations. Green Card/Citizenship Timelines (if you start in 2025) Destination Work Visa PR Timeline Total to Citizenship Cost (₹) Risk US 1–3 yrs 15–20+ yrs 20–35 yrs 40–80L ⚠️⚠️⚠️ Canada ≤3 yrs 1–2 yrs 4–5 yrs 20–40L ⚠️ UK 2–3 yrs 5 yrs 6–7 yrs 25–45L ⚠️⚠️ Australia 2–4 yrs 2–3 yrs 6–7 yrs 25–50L ⚠️⚠️ EU 1–2 yrs 2–5 yrs 6–10 yrs 5–20L ⚠️ US: Challenges & Realities for Indian Students Most Indian students enter on F-1 visas. After graduation, STEM graduates can get up to 3 years of work authorization via OPT (Optional Practical Training), non-STEM: 12 months. Internships during studies (CPT) remain available. However, in 2025, rules are stricter: OPT jobs must closely match your field of study, requiring more documentation. Securing long-term employment means winning an H-1B work visa. Competition is at an all-time high—with only 65,000 + 20000 spots yearly—and preference for higher-salaried, highly skilled roles in tech, finance, and healthcare. Job Market & Trump’s Policies Some US industries (IT, healthcare, renewable energy, finance) still hire international grads—but hiring is down, visa sponsorships are fewer, and legal challenges are higher due to new executive orders focused on stricter immigration control. Many Indian students are struggling to get jobs on completion, despite paying ₹40–80 lakh in tuition and contributing to the US economy. Immigration restrictions and mass layoffs of civil servants have further impacted legal pathways for foreign workers. Canada: The Fastest Route for Indian Graduates Canada offers the Post-Graduation Work Permit (PGWP): work for up to 3 years after study. Canadian experience (1+ year) lets you apply for PR through Express Entry or Provincial Nominee Programs (PNP). Many Indian grads obtain PR within 2–3 years of graduation, sometimes sooner. Citizenship: After receiving PR, you can apply for citizenship after 3 years. High acceptance rates for foreign grads. Transparent, points-based PR system focused on skills, experience, and education. UK: Flexible but Slower Path UK offers the Graduate Route (“PSW”): 2 years (undergrad/master’s) or 3 years (PhD) for work after grad. PR (“Indefinite Leave to Remain”) usually after 5 years on qualifying visas (Tier 2, Skilled Worker), followed by a year for citizenship. Job market is competitive—tech, finance, healthcare fields most welcoming. Australia: Points-Based Pathways After graduation: Temporary Graduate Visa (subclass 485) allows 18 months–4 years’ work, based on qualification. Skilled workers can apply for PR (Subclass 189/190) via a points system—age, English, experience, occupation matter. Most get PR within 2–4 years if occupation is in demand; citizenship follows after 4 years of PR. What Should Aspirants Do in 2025? Top Recommendations Country Key Guidance / Notes US Only pursue if entering high-demand fields (STEM, tech, AI, healthcare) and can afford long timelines for PR. Start networking and preparing for H-1B from day one. Green card backlogs and political climate under Trump remain tough. Canada For most, Canada is the clear winner—fast PR, growing job sectors, and easier route to citizenship. Australia Great for skilled migrants (especially in IT, engineering, healthcare); PR is straightforward if you meet skill demand. UK Flexible, with strong grad work visas and relatively reliable PR in tech, finance, and healthcare. Slightly slower than Canada/Australia for citizenship. Best Master’s Courses for CS Students ( 2025–2030) Country/Region High‑Demand Master’s Specializations (2025–2030) Typical Roles Hired Into Why These Are In Demand (Signals) United States Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning; Data Science & Data Engineering; Cybersecurity; Cloud Computing & Distributed Systems; Computer Vision/NLP; Robotics & Autonomous Systems ML Engineer, Data Scientist/Engineer, Security Engineer/Analyst, Cloud/DevOps Engineer, Computer Vision/NLP Engineer, Robotics/Autonomy Engineer, Software Engineer BLS projects 33% growth for InfoSec Analysts and 36% for Data Scientists; sustained demand for software/cloud and AI talent across tech, finance, healthcare, and government Canada AI & ML; Applied Data Science; Cybersecurity; Cloud & DevOps; Health/Bio‑Informatics; Software Engineering Data Scientist/Engineer, ML Engineer, Security Analyst, Cloud Engineer, MLOps/DevOps, Health Informatics Specialist, Software Engineer Job Bank outlooks show good prospects for cybersecurity and data roles in many provinces; public‑sector digitization and AI adoption driving demand United Kingdom AI & ML; Data Science & Analytics; Cybersecurity; FinTech/Financial Computing; Cloud & Software Systems; Human‑Computer Interaction (UX) ML Engineer, Data/Analytics Engineer, Security Engineer/Analyst, Quant/FinTech Engineer, Cloud/Platform Engineer, UX/Researcher Government and industry reports flag persistent cyber & data skill gaps; rapid AI adoption across sectors; London’s FinTech hub sustains advanced computing demand Australia Cybersecurity; AI & ML; Data Science & Analytics; Cloud/Platform Engineering; Software Engineering; IoT/Embedded Systems Security Specialist, ML/Data Engineer, Cloud/DevOps, Software Engineer, IoT/Embedded Engineer Jobs and Skills Australia lists ICT Security/Analysts/Programmers in shortage; ongoing digitization and cloud migration in public & private sectors European Union (focus: Germany, Ireland, Netherlands) AI & ML; Data Engineering/Analytics; Cybersecurity; Robotics & Autonomous Systems; Embedded/Automotive Software; Cloud & Distributed Systems ML/AI Engineer, Data Engineer, Security Specialist, Robotics/Autonomous Systems Engineer, Embedded/Automotive Software Engineer, Cloud Engineer Cede fop shows sustained growth for ICT professionals; Germany reports 100k+ IT vacancies and long‑term shortages; EU investments in digitalization keep demand elevated
Trump-Putin Alaska Summit: The Untold Reasons Talks Collapsed and What’s Next for the World
The highly anticipated Alaska summit between U.S. President Donald Trump and Russian President Vladimir Putin ended without a truce or any breakthrough toward halting the Ukraine war. In this in-depth analysis, we uncover why the talks collapsed, global reactions, and what this means for India and the world economy. Why Did the Trump-Putin Talks Fail? The Alaska summit was billed as a rare opportunity for a reset amid a grinding and costly conflict. Instead, it concluded with little substance and a sense of deepened deadlock. Here’s why: No Major Concessions: Vladimir Putin stood firm, refusing to consider withdrawals or major concessions. Moscow’s focus stayed on demanding “security guarantees” and NATO’s non-expansion—issues Kyiv and its allies reject as excuses for aggression. America Reluctant to Pressure: President Trump maintained a cautious optimism yet deflected responsibility, suggesting it was ultimately up to Ukraine’s President Zelensky and European leaders to make the tough choices required for a deal. Strategic Calculus: For Putin, the meeting itself ended a period of isolation and restored some diplomatic legitimacy, especially as fighting continued and the West looked for unity Unresolved Core Issues: Despite some hints that land swaps and security assurances were “largely agreed,” the thorniest questions—sovereignty, occupied territory, borders—were not seriously advanced. Ukraine’s Position From Ukraine’s perspective, the Alaska summit delivered neither relief nor reassurance other than heightened sense of being caught between geopolitical bargaining and existential peril. President Zelensky who is under relentless pressure to safeguard Ukrainian sovereignty, maintained that no substantive progress had been made toward a just or lasting peace, stating his opposition to any arrangement involving territorial concessions. Ukrainian leaders and the public alike remain wary that broader negotiations could translate into immense pressure on Kyiv to “make a deal” that contradicts the sacrifices and ambitions of a nation still enduring daily violence and occupation. For many in Kyiv, the summit’s outcome represents a diplomatic interlude that leaves the realities of war unchanged, and may even embolden Russia to press its military and political advantages while the world’s attention is focused on process rather than substance. Europe’s Perspective European leaders swiftly rejected any relaxation of sanctions or settlement that rewards aggression. The EU insists on supporting Ukraine’s sovereignty and territorial integrity, pledging ongoing military and economic aid. There’s relief in Brussels and Kyiv that Trump didn’t force a premature land deal, but also concern that U.S.-EU rifts could worsen if American policy turns too transactional. Impact on Global Politics The failure of the Trump-Putin Alaska summit underscores and deepens the fractures within the international system, reinforcing an era of great power rivalry and diplomatic uncertainty. Rather than bridging divides, the summit revealed the extent to which global politics are now characterized by hardened positions and mutual suspicion. Putin’s appearance on an equal footing with the U.S. president in absence of any concessions offered Moscow a valuable symbolic legitimacy and signaled Russia’s return from diplomatic isolation. Across the Atlantic, the summit exposed subtle but growing discord between the United States and its European allies. Washington’s pragmatic push for a deal clashed with the EU’s insistence on principles and international law. This divergence threatens to weaken the Western coalition that has so far supported Ukraine, introducing new uncertainty about the durability of sanctions and the direction of future diplomatic efforts. In the broader global context, the inconclusive talks send an ambiguous message to other actors—encouraging some to test the boundaries of international order, while leaving vulnerable states more anxious about the reliability of security guarantees and the stability of existing alliances. As hopes for an imminent peace fade, the summit’s failure risks entrenching the conflict as both a local tragedy and a contested front in the larger struggle over the rules and values that govern the international system. Impact on India and World Economy India’s Dilemma: Indian hopes that a peace deal would ease U.S. tariffs and sanctions on Russian oil and fertilizers have been dashed. Instead, Delhi remains in a gray zone, worried about secondary sanctions and their impacts on energy security and trade. Continued Global Uncertainty: The absence of progress means the world will continue to face uncertainty around energy and food prices, especially in Europe, which suffers from high energy premiums and supply risks. Inflationary pressures and market volatility may persist as sanctions stay in place and no end to the war is in sight. Conclusion The failed Trump-Putin summit in Alaska revealed deep divides—not just between Moscow and Kyiv, but also among Western allies who are wrestling with war fatigue and rising global costs. For now, the Ukraine conflict remains unresolved, with little hope for a diplomatic fix in the near term. As the guns continue to speak, the world braces for more turbulence—on the battlefield, in energy markets, and at the highest levels of international diplomacy.
India at 79: Global Strategy, Economic Stakes, and Vision for 2047
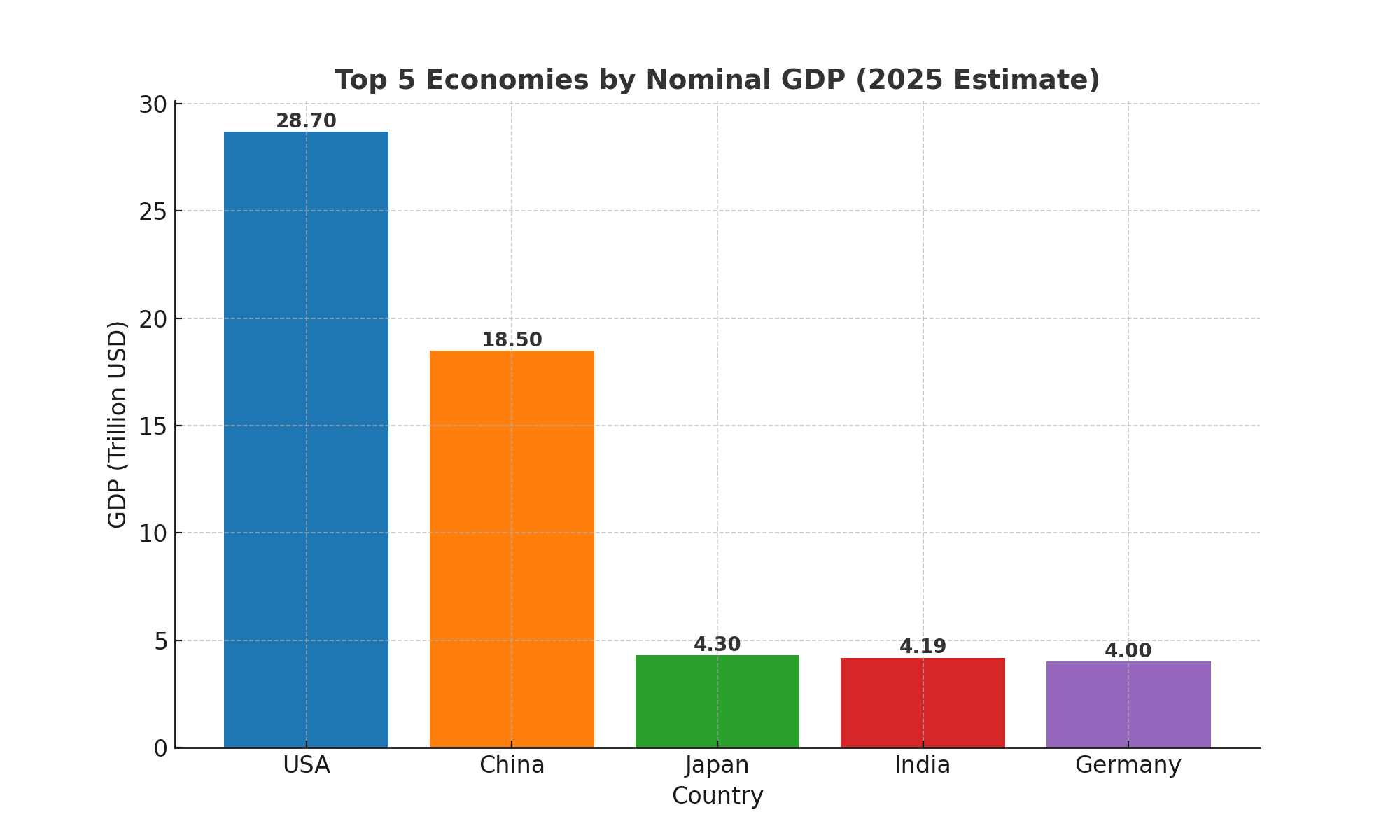
As India approaches its 79th Independence Day, the nation faces a pivotal moment. Its strides in economic growth, digital infrastructure, and global stature are undeniable, yet the pursuit of developed-nation status amid rising geopolitical tensions—China’s assertiveness, Pakistan’s instability, and shifting Western alliances—demands a multi-pronged approach to safeguard India’s future. Recent tensions between India and the United States—arising from trade disagreements, technology export restrictions, and divergent geopolitical priorities, have sparked concerns among citizens about the possible impact on India’s economic growth and global standing. The fear is understandable: the U.S. remains India’s largest trading partner and a key technology collaborator. However, India’s resilience lies in its multi-alignment strategy, which focuses on diversifying partnerships while preserving strategic autonomy. Strengthening trade with the EU, deepening ties within BRICS and the Global South, and leveraging platforms like G20 and Quad can reduce overdependence on any single partner. Additionally, India must boost domestic manufacturing (through PLI schemes), enhance digital self-reliance, and attract FDI through policy stability. These measures will not only shield India from external shocks but also position it as a reliable growth engine in a multipolar world. The key is to view Indo-US ties as vital, but not the sole determinant of India’s destiny. India’s Current Economic Landscape India surpassed the UK to become the 5th largest economy in year 2022. India’s economy is projected to grow at **6.5%-7% in FY 2024-25**, making it one of the fastest-growing major economies. The IMF and World Bank recognize India as a key driver of global growth, contributing over **15% of the world’s incremental GDP**. Sectors like IT, pharmaceuticals, renewable energy, and manufacturing, continue to expand. India as part of key global groups should enhance its geopolitical and economic influence. The *Make in India* and *Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes* have boosted manufacturing, with electronics and defense exports seeing record highs. Today India is the third-largest startup ecosystem globally, with over 100 unicorns .The *Digital India initiative* has transformed financial inclusion, with UPI transactions crossing 10 billion per month. Sector-Wise PLI Allocation & Outcomes Sector PLI Allocation (₹ Cr) Key Outcomes Electronics 40,000 iPhone exports doubled (₹1.2 lakh Cr in 2023) Pharmaceuticals 15,000 35% rise in API production (self-reliance boost) Renewable Energy 24,000 Solar module capacity up 4x (20 GW to 80 GW) Automobiles (EVs) 25,000 EV sales surge (1.5M units in 2023 vs. 0.3M in 2020) Textiles (MMF) 10,000 $5Bn additional exports targeted by 2025 “India is doing wonderfully… I’ve watched a lot of India’s remarkable achievement… India will become the second largest economy of the world overtaking the United States in 10 or 15 years. It will become probably the largest economy in the world in the second half of the 21st century.” – Sachs – Raising Bharat Summit Global Position & GDP Snapshot Metric Value (2025 est.) Global Rank / Insight Nominal GDP ~$4.19 trillion 4th largest (ahead of Japan) GDP (PPP) ~$17.6 trillion 3rd largest globally Q4 YoY Growth 7.4% Among fastest-growing major economies Full-year GDP Growth 6.5% Strong growth performance Global GDP Growth Share ~17% Significant driver of global expansion Focus areas and Their Significance for India’s Economic Growth 1. G20 – Shaping Global Economic Norms Members: Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, France, Germany, India, Indonesia, Italy, Japan, Republic of Korea, Mexico, Russia, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Türkiye, UK, US, plus the European Union & African Union.Why India Benefits: The G20 accounts for 85% of global GDP and 75% of international trade, providing India a powerful platform to influence trade, climate action, digital economy standards, and sustainable finance. 2. BRICS – Alternative Development Architecture Members: Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa (founding); expanded to include Iran, Egypt, Ethiopia, United Arab Emirates, and Indonesia.Why It Matters: Offers India access to the New Development Bank, innovative financial instruments, and enhanced trade and infrastructure collaboration—diversifying away from Western institutions. 3. Global South – Strengthening South-South Solidarity Although the Global South does not have a formal membership, it represents developing nations across Africa, Asia, and Latin America. India as a Leader: Advocating for equitable global policies, debt relief, and technology access positions India as a champion for emerging economies, expanding trade and diplomatic influence. Addressing Internal Security and Migration Challenges Kashmir: Requires development investments, political engagement, and focused security strategies to maintain peace. Migration Pressures: Rohingya and undocumented Bangladeshi migrants raise complex economic and demographic concerns. India needs legal frameworks, robust border management, and regional diplomacy to manage migration effectively. The Way Forward: Integrating Global Strategy with Domestic Reform Deepen engagement in global platforms to secure trade, finance, and technology partnerships. Enhance economic foundations through manufacturing, digital economy, and innovation. Ensure internal stability by addressing security issues and migration challenges. Leverage growth momentum to meet the $30 trillion economy goal by 2047. Conclusion As India celebrates 79 years of independence, its economic journey is marked by resilience and ambition, while challenges like unemployment and bureaucratic delays persist, the country’s demographic dividend, digital revolution, and policy reforms provide a strong foundation. With the right strategies, India can indeed transition from a developing to a developed nation in the coming decades.
H-1B Visa Changes in 2025: From Lottery to Wage-Based Selection – What It Means for Indian Techies
The U.S. H-1B visa program, a gateway for thousands of skilled professionals from India to pursue careers in the United States, is undergoing major changes. The long-standing lottery-based system, which offered equal opportunity to all eligible applicants, is now set to be replaced by a wage-based selection process. This shift could significantly reshape the future of Indian IT professionals, students, and employers aiming for the U.S. tech market. In this article, we compare the old and new systems, analyze the pros and cons, and explore what these changes mean for Indian techies. Current H-1B System (Lottery-Based) Random Lottery Selection: Annually, 85,000 H-1B visas (65,000 for general applicants + 20,000 for advanced degree holders) are awarded via a lottery, giving all eligible applicants an equal chance regardless of seniority or salary. Inclusive Across Wage Levels: Selection has traditionally ignored the salary offered, enabling a level playing field for new graduates, mid-tier roles, and seasoned experts In this article, we explore the complexities of election politics on a global scale, analyzing major elections, international implications, key political movements, and the role of technology in shaping modern governance. Elections serve as the mechanism through which governments are formed and political power is distributed. Their importance lies in. Recent Enhancements (Effective Jan 17, 2025): Expanded Cap-Gap Protection: F-1 students transitioning to H-1B can now maintain status and work authorization up to April 1, up from October 1. After 2025: Students can now stay and work up to April 1 of the following year, even if their OPT ends earlier. Clarified “Specialty Occupation” Definition: Roles now need normally (not universally) require a bachelor’s degree. and the field of study must be directly related to job duties. Strengthened Compliance & Oversight: USCIS can conduct site visits—even at third-party or home offices—and more strictly enforce program integrity. Proposed Changes (Wage-Based Selection) Weighted Selection Over Lottery: The Department of Homeland Security (DHS) is proposing to replace the lottery system with a wage-priority model, ranking applications by salary tiers—favoring higher wages.,(higher wages = better chances). Regulatory Status: The proposal was cleared by the Office of Management and Budget (OMB) on August 8, 2025, and is expected to take effect for the FY 2026 or FY 2027 H-1B season, (applications filed in March 2026 or 2027). Side-by-Side Comparison Feature Current System Proposed System Selection Method Random lottery Wage-tier ranking Fairness Equal opportunity Favors high-salary applicants Entry-Level Impact Moderate (equal chance) Negative—less chance for graduates, lower salaries penalized Employer Strategy Uniform across salary levels Higher-paying offers needed for competitiveness Stability (Cap-Gap) Extended now to April 1 (2025 update) Unchanged Compliance Oversight Strong (as of Jan 2025) Same Is This Good or Bad for Indian Techies? Challenges: -Entry-Level Disadvantage: Fresh graduates and early-career professionals may find it harder to compete without high salaries. They may struggle to secure visas due to lower salary offers. Higher Salary Pressure: Employers, especially startups or smaller firms, may face increased costs to remain competitive. Reward for Expertise: Senior professionals or niche-skilled (e.g., AI, cybersecurity) talent could see improved prospects. Market Alignment: U.S. authorities argue this protects local jobs and ensures fair wages and prioritizes highly skilled talent. Final Thoughts The move from a lottery system to a wage-based selection for H-1B visas is one of the most significant immigration policy shifts in recent years. While it could favor highly paid roles and experienced professionals, it poses fresh challenges for entry-level applicants and cost-conscious employers. Recommendations for Indian Techies: Negotiate Competitive Salaries:Aim for higher wage tiers to improve selection chances. Explore Alternatives:Consider L-1, O-1, or EB-3 visas if H-1B prospects decline. Stay Informed:Monitor USCIS updates for FY 2026/2027 implementation timelines. This policy shift underscores the need for strategic career planning. Adaptability and early preparation will be key to navigating the new landscape.
India’s Defense Superiority: A Comprehensive Analysis on the 79th Independence Day
As India and Pakistan commemorated their 79th Independence Day on August 15th and 14th respectively, the gulf between their defense capabilities has become blatantly obvious—almost to the point of comedy. On the one hand, India quietly cements its position as a global military heavyweight, ranked 4th in the world and modernizing at breakneck speed. On the other, Pakistan’s top brass, exemplified by Field Marshal Asif Munir’s latest performance in the USA, seems more suited for late-night satire than serious strategy. Munir’s bombastic declaration that “if Pakistan goes down, we’ll nuke half the world” might sound chilling—if only it weren’t so ridiculously detached from reality. The actual numbers reveal a far less threatening picture: Pakistan struggles to maintain basic military solvency, with its nuclear arsenal barely at 170 warheads and delivery capabilities largely stuck in the regional league. While Munir may fantasize about global annihilation, Pakistan’s resources are so limited and its dependence on foreign suppliers (especially China) so total that such rants land squarely in the realm of self-parody. In a world where India is exporting advanced weaponry to dozens of countries and operating aircraft carriers and nuclear submarines, perhaps it’s time for Pakistan’s leadership to swap bluster for a bit more realism—because the only thing “global” about Munir’s threat is how widely it’s being laughed at. Operation Sindhoor: India’s Decisive Retaliation In response to the barbaric Pahalgam terror attack that claimed 26 innocent lives, India unleashed Operation Sindhoor on May 7, 2025—a surgical, multi-pronged military strike that thoroughly schooled Pakistan in the art of modern warfare. India’s armed forces demonstrated not only overwhelming superiority but also surgical precision, targeting nine critical terrorist infrastructure sites scattered across Pakistan and Pakistan-occupied Kashmir (PoK). Unlike the usual reckless bluster from Islamabad, these strikes were calculated and meticulous, sparing civilian and military installations while hitting squarely at the nerve centers of Lashkar-e-Taiba (LeT) and Jaish-e-Mohammed (JeM) terror outfits. Yet, despite the clear, humiliating lesson India delivered, Pakistan’s Field Marshal Munir and his cronies have shown zero signs of learning or humility—clinging instead to empty threats and hollow rhetoric while their terror networks lie exposed and crippled. Defense Budget: The Foundation of Military Power India’s defense allocation for 2025-26 stands at $78.7 billion, a 9.5% increase from the previous year. This budget is 8.7 times larger than Pakistan’s $9 billion allocation. Below is a comparative view of defense budgets: Year India (USD Billion) Pakistan (USD Billion) 2020-21 64.1 11.4 2021-22 66.9 10.3 2022-23 70.6 9.5 2023-24 73.8 8.5 2025-26 78.7 9.0 Manpower and Military Strength India maintains a decisive advantage in human resources with 1.45 million active military personnel compared to Pakistan’s 654,000, representing a 2.2x superiority. This advantage extends to reserve forces, where India commands 1.15 million reserves against Pakistan’s 550,000. The total available manpower pool further emphasizes India’s demographic advantage, with approximately 662 million available compared to Pakistan’s 108 million. The Indian Armed Forces, recognized as the world’s second-largest military force with the largest volunteer army, benefits from India’s population of over 1.4 billion. This massive human resource base ensures sustained recruitment and operational capability across multiple theaters. Air Power: Technological Superiority in the Skies India’s air superiority is evident across multiple dimensions. The Indian Air Force operates 513 fighter jets compared to Pakistan’s 328, and maintains a total aircraft fleet of 2,229 versus Pakistan’s 1,399. More importantly, India possesses qualitatively superior platforms including 36 French Rafale fighters equipped with Meteor long-range air-to-air missiles, SCALP cruise missiles, and advanced AESA radars. The IAF’s backbone consists of approximately 272 Su-30MKI fighters, supplemented by indigenous Tejas aircraft and various other platforms. Pakistan’s air force relies primarily on the JF-17 Thunder (co-developed with China), F-16 Fighting Falcons, and recently acquired J-10C fighters from China. However, the recent Operation Sindhoor in May 2025 demonstrated India’s technological edge. India’s force multipliers include Phalcon AWACS, Netra AEW&C systems, and advanced ground-based air defense networks featuring S-400, Barak-8, and indigenous Akash systems. Pakistan operates fewer AWACS platforms and relies heavily on Chinese-supplied air defense systems. Naval Dominance: Command of the Seas India’s maritime superiority is overwhelming. The Indian Navy operates 293 naval vessels compared to Pakistan’s 121. Most significantly, India maintains two aircraft carriers (INS Vikramaditya and the indigenous INS Vikrant) while Pakistan operates none. India’s surface fleet includes 12 destroyers and 15 frigates, vastly outgunning Pakistan’s 11 frigates and zero destroyers. The submarine advantage is equally pronounced, with India operating 18 submarines including 2 nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarines (INS Arihant class), while Pakistan maintains only 8 conventional submarines. During the recent tensions in May 2025, India’s naval deployment effectively demonstrated its ability to project power and enforce maritime dominance, with INS Vikrant leading a 36-ship armada that effectively deterred Pakistani naval operations. Nuclear Capabilities: Strategic Parity with Tactical Advantages Both nations maintain substantial nuclear arsenals, with India possessing 180 nuclear warheads compared to Pakistan’s 170 as of January 2025. However, India’s nuclear triad is more advanced, featuring land-based Agni missiles (range up to 5,000+ km), sea-based capabilities from nuclear submarines, and air-delivered weapons. India’s recent testing of the Agni-V MIRV (Multiple Independently Targetable Reentry Vehicle) capability and development of the Agni-VI (projected 6,000+ km range) demonstrates its advancing strategic reach. Pakistan’s nuclear arsenal remains primarily land-based, though it is developing sea-based capabilities with the Babur-3 submarine-launched cruise missile. Indigenous Production: Self-Reliance vs Dependency India has achieved remarkable progress in defense indigenization, with indigenous content reaching 65% and defense production hitting a record ₹1.27 lakh crore in FY 2023-24. India’s defense exports have surged 34-fold from ₹686 crore in 2013-14 to ₹23,622 crore ($2.8 billion) in 2024-25, with exports reaching over 80 countries. Key indigenous achievements include the Tejas Light Combat Aircraft, BrahMos cruise missiles, INS Vikrant aircraft carrier, Akash air defense systems, and Advanced Towed Artillery Gun Systems (ATAGS). India is also developing the fifth-generation Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA) and has begun production of AK-203 assault rifles with increasing indigenous content. In stark contrast, Pakistan depends on China for 81% of its arms imports. This
US and EU Still Trade with Russia While Targeting India: A Tale of Hypocrisy Backed by Numbers
Since the Ukraine war began in 2022, the US and European Union have repeatedly criticized India’s continued imports of Russian oil. The most recent escalation came in August 2025, when President Donald Trump announced new tariffs on India, citing its trade ties with Russia. However, a closer look at trade data exposes a double standard—the US and EU themselves still conduct billions in trade with Russia even as they target India diplomatically and economically Though US and EU keep on blaming India of the oil purchases, the conflict in Ukraine has sparked fierce debate about whether Western actions—especially NATO expansion—provoked Russia, and whether the enormous sums now being spent to support Ukraine reflect strategic sense or misguided policy A significant number of respected analysts and officials, including historians and policy architects from the Cold War era, have long warned that NATO’s steady eastward expansion would eventually provoke a backlash from Russia. Pushing military alliances up to Russia’s borders would be seen in Moscow as a direct threat, making conflict a realty in a sense the NATOs open door policy is mainly responsible for the Russia, Ukraine conflict Does USA a really want a quick end to this conflict is debatable as U.S. defense manufacturers—including giants like Lockheed Martin, Raytheon, and Boeing—have seen surging demand. Lockheed Martin, for instance, doubled Javelin missile production from ~2,100 to ~4,000 units annually. Rising oil and gas prices since the conflict have driven inflation—but also created a boom in U.S. LNG and crude exports. U.S. LNG shipments to Europe more than doubled in 2022, positioning the U.S. as the top LNG exporter globally Chart: US & EU Imports from Russia (2022–2025) Year US Imports from Russia (USD) EU Imports from Russia (USD) 2022 $14.1 billion $112 billion 2023 $8.7 billion $69 billion 2024 $3.0 billion $29 billion 2025 (H1) $2.5 billion (est.) ~$17 billion (est.) Is India’s Russian Oil Imports: A Market-Driven Necessity? Indian officials argue that energy sourcing is not ideological, but based on national interest—just as it is for Europe and the US. Indian officials note that purchasing Russian oil has played a stabilizing role in global energy markets and prevented sharper price rises that would have adversely affected developing economies. India has consistently rebuffed Western pressure to reduce imports, emphasizing its right to pursue market-driven purchases and secure the best terms for its economy. India has maintained steady oil imports from Russia due to affordable pricing, refinery compatibility, and energy security needs. In July 2025, India imported 1.58 million barrels/day, down from peak levels but still substantial. In a controversial move, Trump imposed an additional 25% tariff on Indian exports, raising the total tariff rate to 50%. The stated reason: India is “funding Putin’s war” by purchasing discounted Russian crude. India called the move “unjustified and damaging to trust”. It highlighted that the West itself continues Russian trade while blaming others and asserted its sovereign right to procure energy based on national interest. In a now-viral social media post, Trump equated India and Russia as “dead economies”, triggering outrage among Indian citizens, media, and policymakers: “You can’t win a war when you’re backed by dead economies like India and Russia. We need real allies, not freeloaders.” – Trump, August 2025.Officials labeled the tweet “deeply disrespectful”, and commentators called it a “slap in the face” after years of building Indo-US ties. Strategic experts warn it may erode trust and strain cooperation in QUAD and Indo-Pacific partnerships. Visual Comparison: Who Still Trades with Russia? Country/Bloc Key Russian Imports Still Ongoing EU LNG (16.5M tons in 2024), fertilizers, critical metals USA Uranium, palladium, platinum, fertilizers India Crude oil (1.58M barrels/day), minor fertilizers Conclusion India’s embrace of Russian oil is a direct result of market forces: discounted supplies, urgent domestic needs, and an opportunity to enhance refining profits through exports. This strategy has shielded India from global price spikes, allowed cost-effective fuel for its growing economy, and maintained a degree of strategic autonomy amid shifting geopolitical winds. Notably, this pragmatic approach aligns with the West’s own initial intention to cap, not curtail, Russian oil exports so as to maintain price stability, benefiting India and global consumers alike The current geopolitical drama reveals a stark contradiction: the West publicly chastises India for its energy choices, yet it quietly maintains its own trade ties with Russia. As diplomatic tensions rise, the focus should be on consistent policy across partners—or risk undermining credibility and fuelling deeper mistrust.
India’s Russian Oil Strategy vs NATO Sanction Threats: Global Trade Tensions Explained
Amid escalating tensions over the Russia-Ukraine conflict, NATO Secretary General Mark Rutte recently issued a warning to countries like India, China, and Brazil about the potential for secondary sanctions and 100% tariffs if they continue trading with Russia—especially in the energy sector. This article explores the impact of such threats, India’s energy strategy, and the wider global oil trade realignments. NATO, traditionally a defense alliance, stepped into unfamiliar territory when its chief warned of potential sanctions against countries engaging in oil trade with Russia. Indian officials responded firmly, emphasizing the alliance has no legal authority to direct sovereign economic policies. India continues to prioritize energy security over external pressure, asserting its right to diversify energy sources and secure discounted oil from Russia for economic stability. India has ramped up Russian oil imports from under 1% pre-2022 to nearly 40% in 2024. For China, it ensures supply security. Brazil views the trade as a diversification tool. All three economies benefit from discounted crude amid a volatile market, balancing fiscal responsibility with geopolitical pragmatism. Global Oil Trade Trends: Fig : Russian Oil Imports by India, China, and Brazil (2022–2024) Impact of U.S. Sanctions on Global Oil Trade U.S. sanctions on Russia, Iran, and Venezuela have reshaped global energy markets. These restrictions disrupted traditional supply lines and increased energy costs. Countries like India had to navigate shifting trade routes, rising freight charges, and volatile prices—prompting a reorientation of oil imports to ensure stable supply from multiple partners, including Russia. The Double Standard: Europe’s Ongoing Russian Imports Summary of Key Impacts Issue Description Relevant for India? NATO’s mandate on sanctions NATO lacks formal authority on international trade enforcement. Not directly applicable US sanctions on major producers Disrupt global oil markets, raise costs, and increase volatility. High impact India’s oil import strategy Diversification and discounted Russian oil ensure energy security. Essential European hypocrisy on Russian imports European nations continue partial imports despite rhetoric. Raises fairness concerns While India faces criticism for continuing Russian oil imports, some European nations have quietly maintained Russian energy flows—albeit at reduced levels. This has triggered concerns over fairness and geopolitical bias in enforcement of sanctions. Critics argue that developing nations are being unfairly targeted for practices also followed in the West. India’s Path Forward India, as a large developing nation, must prioritize secure, affordable energy imports and has logical grounds for sourcing oil based on economic needs but not on external political pressures. Switching from discounted Russian oil to higher-priced alternatives would increase production and transportation costs, fueling inflation in both economies. As India depends on imports for over 85% of its crude needs, even a small price differential can have an outsized impact on consumer prices and economic stability Proposed US bills threaten not just to target oil trade, but to impose secondary tariffs on all exports from countries transacting with Russia. This could result in tariffs of up to 100% or even 500% on Indian and Chinese goods entering the US. Both countries are major exporters to the US, so such measures would threaten key sectors such as manufacturing and technology, putting jobs and economic growth at risk. US sanctions would force Indian and Chinese refiners to quickly diversify suppliers amid an already volatile market, potentially leading to logistical challenges, increased freight costs, and supply shortages. This fracturing of global oil supply chains could increase operational uncertainty for businesses and governments alike US sanctions on the oil trade do not just affect Russia—they inject additional instability into global energy and financial markets, making economic planning more difficult for major oil importers, including India and China. This volatility weighs on their broader growth trajectories and policy autonomy While geopolitical alliances like NATO may raise concerns, India is unlikely to compromise on its national interest. A possible way forward lies in diplomatic engagement, strengthening multilateral platforms like BRICS and G20 to ensure global energy equity, and pursuing long-term diversification through renewables and regional partnerships.
U.S.-India Strategic Priorities and Red Lines: Navigating Trade, Tech, Geopolitical Challenges and FTA
As India and the United States deepen their strategic partnership in the 21st century, understanding the driving forces and constraints behind their policymaking becomes essential. From geopolitics to technology and climate cooperation, the two democracies are building bridges—but also navigating sensitive differences. while navigating sensitive differences. Let us explore how their priorities align or diverge, framed around key goals and red lines. Domain U.S. Priorities India’s Priorities U.S. Red Lines India’s Red Lines Geopolitics Contain China’s influence in Indo-Pacific; support allies like Japan, Taiwan Maintain strategic autonomy; balance China without direct confrontation Strong support for Russia or Iran Being pressured into fall into a geopolitical block Defense Deepen interoperability via QUAD, joint exercises, arms sales Build indigenous defense capability while partnering with U.S. & others Technology transfer without safeguards Loss of defense sovereignty; foreign boots on Indian soil Trade & Economy Market access, IPR enforcement, reduce tariffs on U.S. goods Greater access to U.S. markets for services, skilled labor; resist overregulation Data localization, protectionism, regulatory unpredictability Concessions without reciprocity Technology Lead in critical and emerging tech (AI, semiconductors); promote open internet Build self-reliance (Atmanirbhar Bharat) in key tech sectors Restrictions on American firms or IP theft Overdependence on U.S. tech; loss of digital sovereignty Climate & Energy Global emissions cuts, clean tech leadership, carbon pricing Climate finance, equitable responsibility, energy security Opposition to U.S. oil/gas sanctions or bypass of energy cooperation Pressure to cut coal without aid; unequal emission cuts Russia-Ukraine Isolate Russia diplomatically and economically Maintain ties with Russia (arms, energy); avoid taking sides Support for Russia in multilateral forums Being forced to condemn Russia or reduce energy imports Indo-Pacific Promote “Free and Open Indo-Pacific” via alliances and deterrence Inclusive Indo-Pacific vision; prefer multipolarity, no direct confrontation Undermining alliances like AUKUS, QUAD Being drawn into military alliances or containment strategies Human Rights / Values Promote democracy, religious freedom, press freedom Emphasize pluralism, but resist external pressure on internal issues Systemic human rights violations by partners External criticism of domestic policies (Kashmir, CAA, etc.) Strategic Takeaways The U.S.-India relationship is increasingly defined by both convergence and constraint. While the two nations align on shared concerns—particularly regarding China’s assertiveness, defense cooperation, and a stable Indo-Pacific region—they remain cautious about overcommitting. India’s principle of strategic autonomy, for instance, often puts it at odds with Washington’s expectation of coalition loyalty. Meanwhile, Washington’s emphasis on values-based diplomacy sometimes clashes with New Delhi’s desire for non-interference in domestic affairs. Still, the momentum in bilateralcooperation remains strong, especially in defense tech, climate innovation, and digital infrastructure. The future of this partnership will depend on both sides respecting each other’s red lines while maximizing areas of mutual interest. Latest Concerns on U.S.-India Free Trade Agreement Talks Despite strong bilateral ties, progress on a formal U.S.-India Free Trade Agreement (FTA) has remained elusive. Recent concerns on both sides reflect deep-rooted issues in market access, regulatory transparency, and strategic industries. For the U.S., there is growing frustration over India’s high tariffs, data localization policies, and intellectual property protections. Washington also seeks more predictability for American companies investing in India, particularly in digital services and manufacturing.Conversely, India is cautious about opening its markets too broadly without reciprocal access for its skilled labor and agricultural exports. New Delhi is also concerned about potential erosion of sovereignty through externally imposed standards on labor, environment, and e-commerce. While there have been some positive developments—such as partial resolution of WTO disputes and expanding sectoral cooperation—the FTA remains stalled, underscoring the challenges of reconciling protectionist impulses with aspirations for deeper integration. Going forward, the success of the U.S.-India partnership will depend on balancing ambition with realism. Both sides must accept that full alignment on all issues is unlikely—but that doesn’t preclude meaningful progress in areas where convergence is strong. Sustained dialogue, respect for strategic autonomy, and a shared commitment to democratic norms will be critical to turning potential into enduring policy outcomes. Tags India-US relations, US India trade, India foreign policy, US Indo-Pacific strategy, Free Trade Agreement India US, US India defense ties, geopolitics Asia, strategic autonomy, QUAD, technology cooperation India US, global trade policy, climate diplomacy You Might Be Interested In
Mastering the Art of Work-Life Effectively
Elections are a crucial part of global politics, influencing the direction of nations, shaping international relations, and determining the balance of power across continents. In an interconnected world, electoral outcomes do not merely impact domestic affairs; they also have far-reaching consequences on trade agreements, military alliances, diplomatic relations, and economic stability. The intersection of national elections and global politics has become more evident than ever, with the rise of digital campaigning, foreign influence, and shifting political ideologies across regions. In this article, we explore the complexities of election politics on a global scale, analyzing major elections, international implications, key political movements, and the role of technology in shaping modern governance. Elections serve as the mechanism through which governments are formed and political power is distributed. Their importance lies in: Representation: Citizens elect leaders who represent their interests and values in government. Accountability: Leaders are held responsible for their actions, knowing they can be voted out if they fail to meet expectations. Public Participation: Encourages civic engagement and ensures that diverse voices contribute to governance. Legitimacy: Establishes the credibility of governments, reinforcing stability and trust in institutions. In this article, we explore the complexities of election politics on a global scale, analyzing major elections, international implications, key political movements, and the role of technology in shaping modern governance. Elections serve as the mechanism through which governments are formed and political power is distributed. Their importance lies in. Major Elections That Shape Global Politics In this article, we explore the complexities of election politics on a global scale, analyzing major elections, international implications, key political movements, and the role of technology in shaping modern governance. Elections serve as the mechanism through which governments are formed and political power is distributed. Their importance lies in. You Might Be Interested In All Posts Politics The Role of Media in Shaping Political Narratives Behind the Scenes of International Political Deals The Truth About Political Power and Influence How Modern Elections Shape the Future The Hidden Forces Behind Global Political Shifts In this article, we explore the complexities of election politics on a global scale, analyzing major elections, international implications, key political movements, and the role of technology in shaping modern governance. Elections serve as the mechanism through which governments are formed and political power is distributed. Their importance lies in. With globalization, national elections are no longer isolated events; foreign governments, corporations, and organizations often play a role in shaping. – The Royal Times In this article, we explore the complexities of election politics on a global scale, analyzing major elections, international implications, key political movements, and the role of technology in shaping modern governance. Elections serve as the mechanism through which governments are formed and political power is distributed. Their importance lies in. In this article, we explore the complexities of election politics on a global scale, analyzing major elections, international implications, key political movements, and the role of technology in shaping modern governance. Elections serve as the mechanism through which governments are formed and political power is distributed. Their importance lies in: In this article, we explore the complexities of election politics on a global scale, analyzing major elections, international implications, key political movements, and the role of technology in shaping modern governance. Elections serve as the mechanism through which governments are formed and political power is distributed. Their importance lies in: Digital Propaganda and Cyber Warfare In this article, we explore the complexities of election politics on a global scale, analyzing major elections, international implications, key political movements, and the role of technology in shaping modern governance. Elections serve as the mechanism through which governments are formed and political power is distributed. Their importance lies in: Technology has transformed the way elections are conducted and how political campaigns are run. From digital voting systems to AI-driven analytics, the role of technology in elections cannot be ignored. In this article, we explore the complexities of election politics on a global scale, analyzing major elections, international implications, key political movements, and the role of technology in shaping modern governance. Elections serve as the mechanism through which governments are formed and political power is distributed. Their importance lies in:
The Impact of Technology on Business Innovation
Elections are a crucial part of global politics, influencing the direction of nations, shaping international relations, and determining the balance of power across continents. In an interconnected world, electoral outcomes do not merely impact domestic affairs; they also have far-reaching consequences on trade agreements, military alliances, diplomatic relations, and economic stability. The intersection of national elections and global politics has become more evident than ever, with the rise of digital campaigning, foreign influence, and shifting political ideologies across regions. In this article, we explore the complexities of election politics on a global scale, analyzing major elections, international implications, key political movements, and the role of technology in shaping modern governance. Elections serve as the mechanism through which governments are formed and political power is distributed. Their importance lies in: Representation: Citizens elect leaders who represent their interests and values in government. Accountability: Leaders are held responsible for their actions, knowing they can be voted out if they fail to meet expectations. Public Participation: Encourages civic engagement and ensures that diverse voices contribute to governance. Legitimacy: Establishes the credibility of governments, reinforcing stability and trust in institutions. In this article, we explore the complexities of election politics on a global scale, analyzing major elections, international implications, key political movements, and the role of technology in shaping modern governance. Elections serve as the mechanism through which governments are formed and political power is distributed. Their importance lies in. Major Elections That Shape Global Politics In this article, we explore the complexities of election politics on a global scale, analyzing major elections, international implications, key political movements, and the role of technology in shaping modern governance. Elections serve as the mechanism through which governments are formed and political power is distributed. Their importance lies in. You Might Be Interested In All Posts Politics The Role of Media in Shaping Political Narratives Behind the Scenes of International Political Deals The Truth About Political Power and Influence How Modern Elections Shape the Future The Hidden Forces Behind Global Political Shifts In this article, we explore the complexities of election politics on a global scale, analyzing major elections, international implications, key political movements, and the role of technology in shaping modern governance. Elections serve as the mechanism through which governments are formed and political power is distributed. Their importance lies in. With globalization, national elections are no longer isolated events; foreign governments, corporations, and organizations often play a role in shaping. – The Royal Times In this article, we explore the complexities of election politics on a global scale, analyzing major elections, international implications, key political movements, and the role of technology in shaping modern governance. Elections serve as the mechanism through which governments are formed and political power is distributed. Their importance lies in. In this article, we explore the complexities of election politics on a global scale, analyzing major elections, international implications, key political movements, and the role of technology in shaping modern governance. Elections serve as the mechanism through which governments are formed and political power is distributed. Their importance lies in: In this article, we explore the complexities of election politics on a global scale, analyzing major elections, international implications, key political movements, and the role of technology in shaping modern governance. Elections serve as the mechanism through which governments are formed and political power is distributed. Their importance lies in: Digital Propaganda and Cyber Warfare In this article, we explore the complexities of election politics on a global scale, analyzing major elections, international implications, key political movements, and the role of technology in shaping modern governance. Elections serve as the mechanism through which governments are formed and political power is distributed. Their importance lies in: Technology has transformed the way elections are conducted and how political campaigns are run. From digital voting systems to AI-driven analytics, the role of technology in elections cannot be ignored. In this article, we explore the complexities of election politics on a global scale, analyzing major elections, international implications, key political movements, and the role of technology in shaping modern governance. Elections serve as the mechanism through which governments are formed and political power is distributed. Their importance lies in: