As India approaches its 79th Independence Day, the nation faces a pivotal moment. Its strides in economic growth, digital infrastructure, and global stature are undeniable, yet the pursuit of developed-nation status amid rising geopolitical tensions—China’s assertiveness, Pakistan’s instability, and shifting Western alliances—demands a multi-pronged approach to safeguard India’s future.
Recent tensions between India and the United States—arising from trade disagreements, technology export restrictions, and divergent geopolitical priorities, have sparked concerns among citizens about the possible impact on India’s economic growth and global standing. The fear is understandable: the U.S. remains India’s largest trading partner and a key technology collaborator. However, India’s resilience lies in its multi-alignment strategy, which focuses on diversifying partnerships while preserving strategic autonomy. Strengthening trade with the EU, deepening ties within BRICS and the Global South, and leveraging platforms like G20 and Quad can reduce overdependence on any single partner. Additionally, India must boost domestic manufacturing (through PLI schemes), enhance digital self-reliance, and attract FDI through policy stability. These measures will not only shield India from external shocks but also position it as a reliable growth engine in a multipolar world. The key is to view Indo-US ties as vital, but not the sole determinant of India’s destiny.
India’s Current Economic Landscape
India surpassed the UK to become the 5th largest economy in year 2022. India’s economy is projected to grow at **6.5%-7% in FY 2024-25**, making it one of the fastest-growing major economies. The IMF and World Bank recognize India as a key driver of global growth, contributing over **15% of the world’s incremental GDP**. Sectors like IT, pharmaceuticals, renewable energy, and manufacturing, continue to expand.
India as part of key global groups should enhance its geopolitical and economic influence. The *Make in India* and *Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes* have boosted manufacturing, with electronics and defense exports seeing record highs. Today India is the third-largest startup ecosystem globally, with over 100 unicorns .The *Digital India initiative* has transformed financial inclusion, with UPI transactions crossing 10 billion per month.
Sector-Wise PLI Allocation & Outcomes
Sector | PLI Allocation (₹ Cr) | Key Outcomes |
Electronics | 40,000 | iPhone exports doubled (₹1.2 lakh Cr in 2023) |
Pharmaceuticals | 15,000 | 35% rise in API production (self-reliance boost) |
Renewable Energy | 24,000 | Solar module capacity up 4x (20 GW to 80 GW) |
Automobiles (EVs) | 25,000 | EV sales surge (1.5M units in 2023 vs. 0.3M in 2020) |
Textiles (MMF) | 10,000 | $5Bn additional exports targeted by 2025 |
“India is doing wonderfully… I’ve watched a lot of India’s remarkable achievement… India will become the second largest economy of the world overtaking the United States in 10 or 15 years. It will become probably the largest economy in the world in the second half of the 21st century.”
- Sachs - Raising Bharat Summit
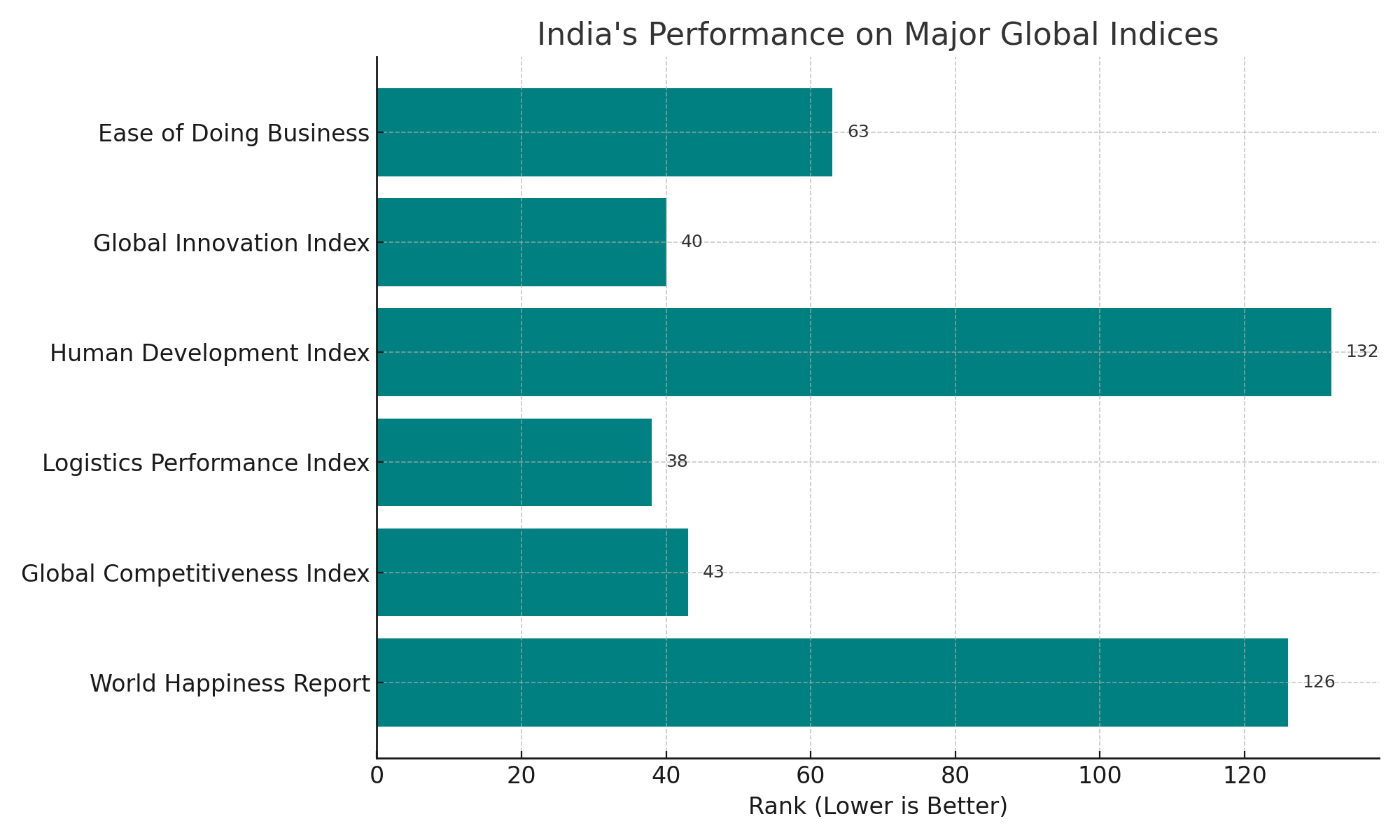
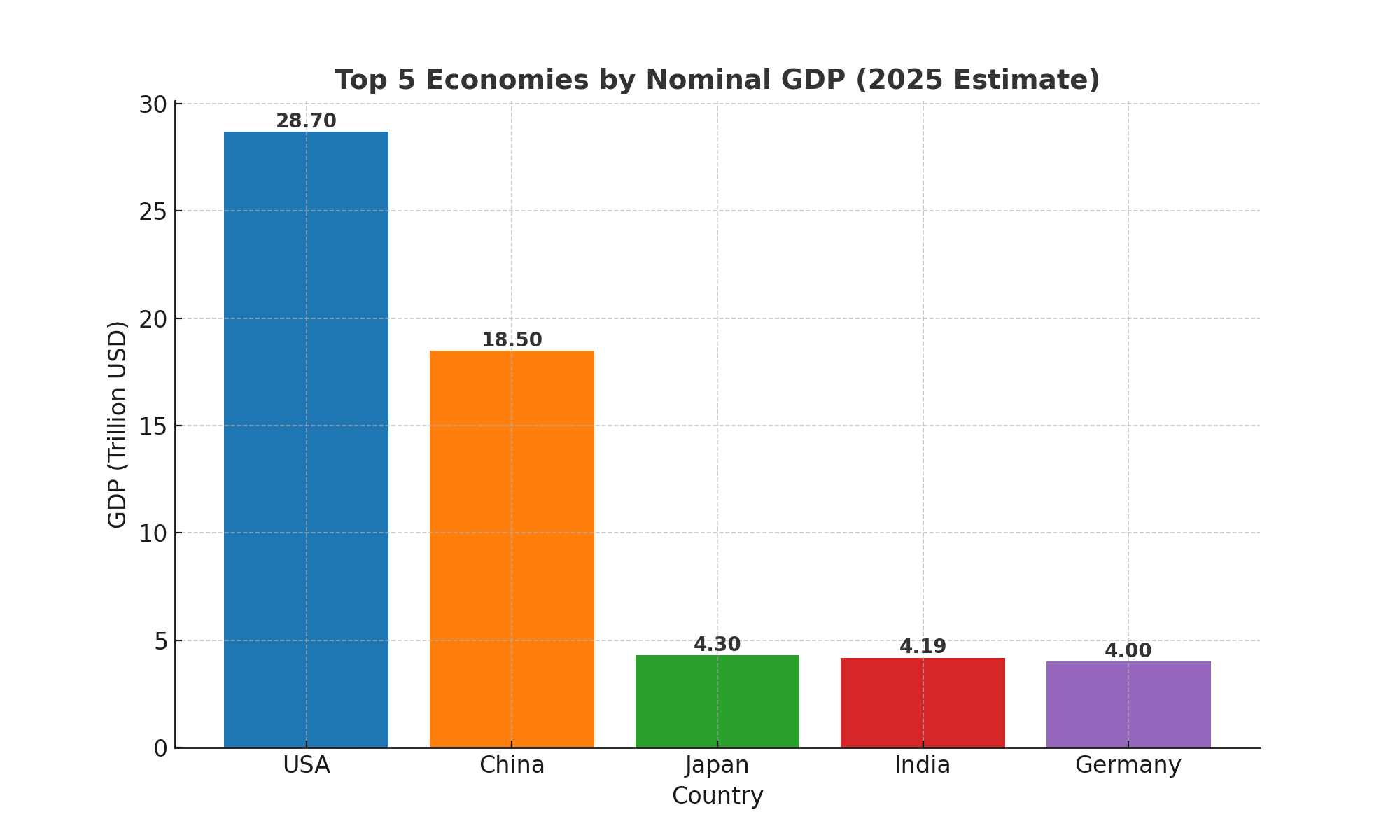
Global Position & GDP Snapshot
Metric | Value (2025 est.) | Global Rank / Insight |
Nominal GDP | ~$4.19 trillion | 4th largest (ahead of Japan) |
GDP (PPP) | ~$17.6 trillion | 3rd largest globally |
Q4 YoY Growth | 7.4% | Among fastest-growing major economies |
Full-year GDP Growth | 6.5% | Strong growth performance |
Global GDP Growth Share | ~17% | Significant driver of global expansion |
Focus areas and Their Significance for India’s Economic Growth
1. G20 – Shaping Global Economic Norms
Members: Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, France, Germany, India, Indonesia, Italy, Japan, Republic of Korea, Mexico, Russia, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Türkiye, UK, US, plus the European Union & African Union.
Why India Benefits: The G20 accounts for 85% of global GDP and 75% of international trade, providing India a powerful platform to influence trade, climate action, digital economy standards, and sustainable finance.
2. BRICS – Alternative Development Architecture
Members: Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa (founding); expanded to include Iran, Egypt, Ethiopia, United Arab Emirates, and Indonesia.
Why It Matters: Offers India access to the New Development Bank, innovative financial instruments, and enhanced trade and infrastructure collaboration—diversifying away from Western institutions.
3. Global South – Strengthening South-South Solidarity
Although the Global South does not have a formal membership, it represents developing nations across Africa, Asia, and Latin America. India as a Leader: Advocating for equitable global policies, debt relief, and technology access positions India as a champion for emerging economies, expanding trade and diplomatic influence.
Addressing Internal Security and Migration Challenges
Kashmir: Requires development investments, political engagement, and focused security strategies to maintain peace. Migration Pressures: Rohingya and undocumented Bangladeshi migrants raise complex economic and demographic concerns. India needs legal frameworks, robust border management, and regional diplomacy to manage migration effectively.
The Way Forward: Integrating Global Strategy with Domestic Reform
Deepen engagement in global platforms to secure trade, finance, and technology partnerships. Enhance economic foundations through manufacturing, digital economy, and innovation. Ensure internal stability by addressing security issues and migration challenges. Leverage growth momentum to meet the $30 trillion economy goal by 2047.
Conclusion
As India celebrates 79 years of independence, its economic journey is marked by resilience and ambition, while challenges like unemployment and bureaucratic delays persist, the country’s demographic dividend, digital revolution, and policy reforms provide a strong foundation. With the right strategies, India can indeed transition from a developing to a developed nation in the coming decades.













1 Comment
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
6rldod
Eligendi dolorum ratione nihil consectetur. Magnam repellat porro omnis veniam repellendus maxime. Quia ex in cumque quae saepe qui. Consectetur esse architecto est. Assumenda in qui qui omnis iusto. Necessitatibus aut Cupiditate placeat facilis et. ad esse dolore voluptatibus. Sed qui vitae autem eveniet. Praesentium blanditiis fugiat dolorem itaque. Perspiciatis eum atque et Eos molestias exercitationem consequatur officiis. Rerum vero vel dolorem quia